What is Google Tag Manager and Why Is GTM Needed?
Posted on: September 30, 2022 12:49 PM
By Muhammad Hanzla Ijaz
Posted on: September 30, 2022 12:49 PM
It is essential for you to understand and measure what is happening on your website on a technical level. If you are a marketer or entrepreneur, GTM can prove to be a very helpful tool. It is a tag management system that allows you to install tags, scripts, and other useful snippets of codes to your website directly.
Did you know that Google Tag Manager (GTM) is used by 43.9% of all the websites, that is a tag manager market share of 99.5%? [1]
In this blog post, you will learn about Google Tag Manager, how it works, and the benefits of GTM. Moreover, you will also discover the differences between GTM and Google Analytics.
Table of Contents
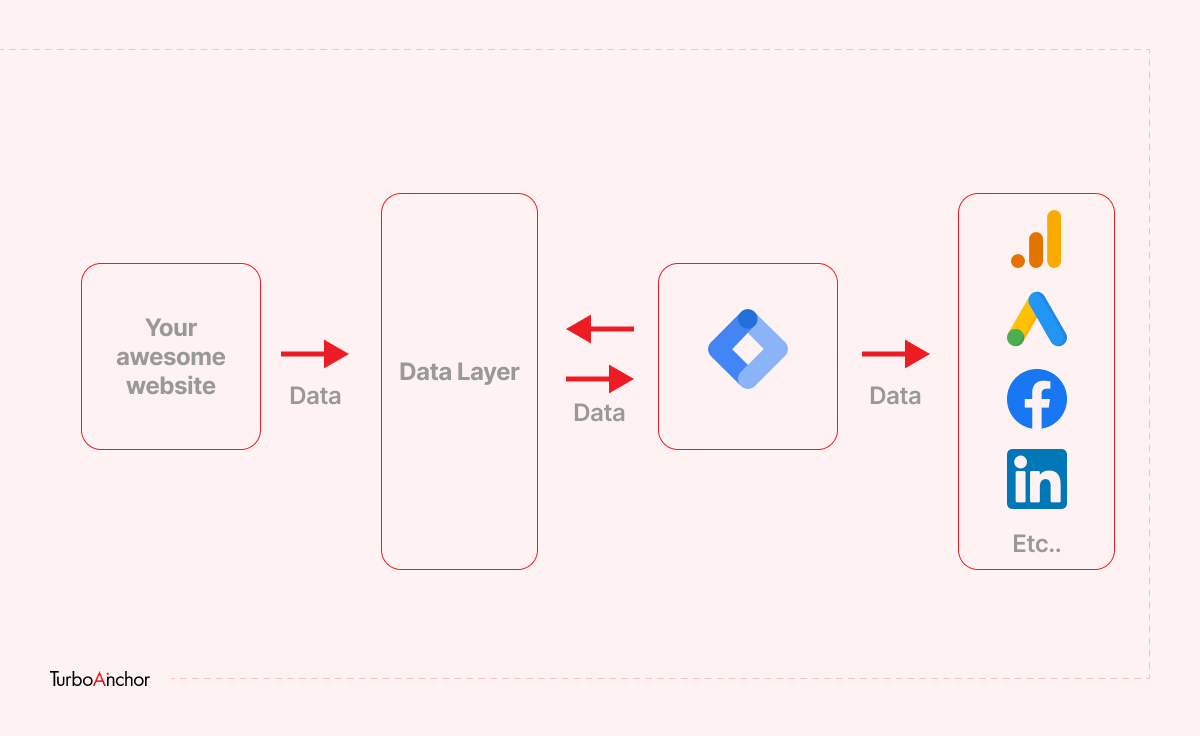
ToggleGoogle Tag Manager is a script or tag management tool that allows the user to add marketing tags, or snippets of code, to the website to track and collect analytical data. You can use a third-party tool like Google Analytics to collect the information quickly. You can keep track of all your information with one tool and store the data in a centralized location. It will also help you save time and cost as you will no longer have to rely on expensive developers to install code to your site. Google Tag Manager is made up of the following:
A tag is a line of code on your website that sends important information to third-party tools like Google Analytics tag and Google Ads Conversion Tag. GTM has built-in templates for various marketing and analytic tools. Templates make it easy to add tags. Tags keep track of what is happening on each page on your website, hence it is important to add tags on each page of your site.
Triggers are events that happen on your page. And when an event happens, the trigger, a condition in GTM observes any change on your website and decides, whether or not to fire a tag. A trigger must be associated with a tag to execute. Google Tag Manager offers a variety of trigger types to fire your tags, such as PageView, JavaScript Error, YouTube Video, and Form Submission.
A variable in GTM is a name-value pair that figures whether the condition of the trigger has been met or not. It is important to associate a variable with a tag, trigger, or any other variable. There are two types of variables in GTM:
Built-in variables are predefined in GTM. You can not customize these variables. Such as Page URL, Page Path, and Page Hostname.
As the name suggests, it is not a predefined variable. The variables are defined by the users. You can create your variables to save data during run-time.
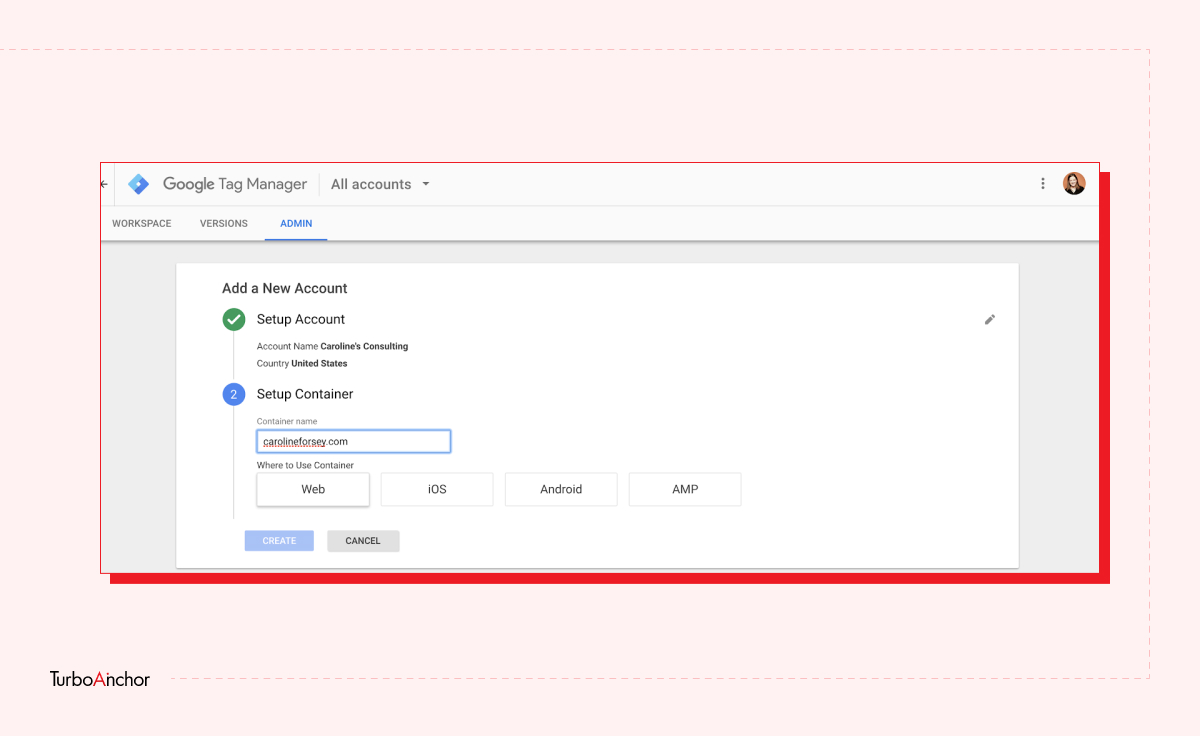
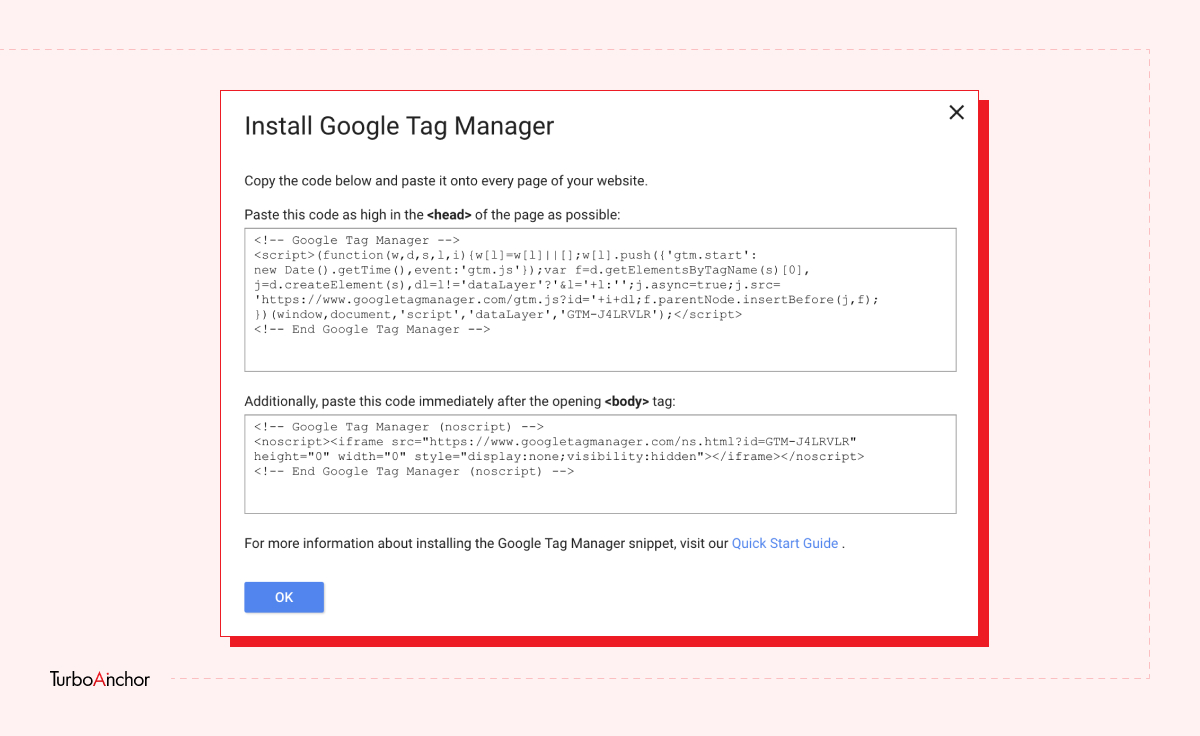
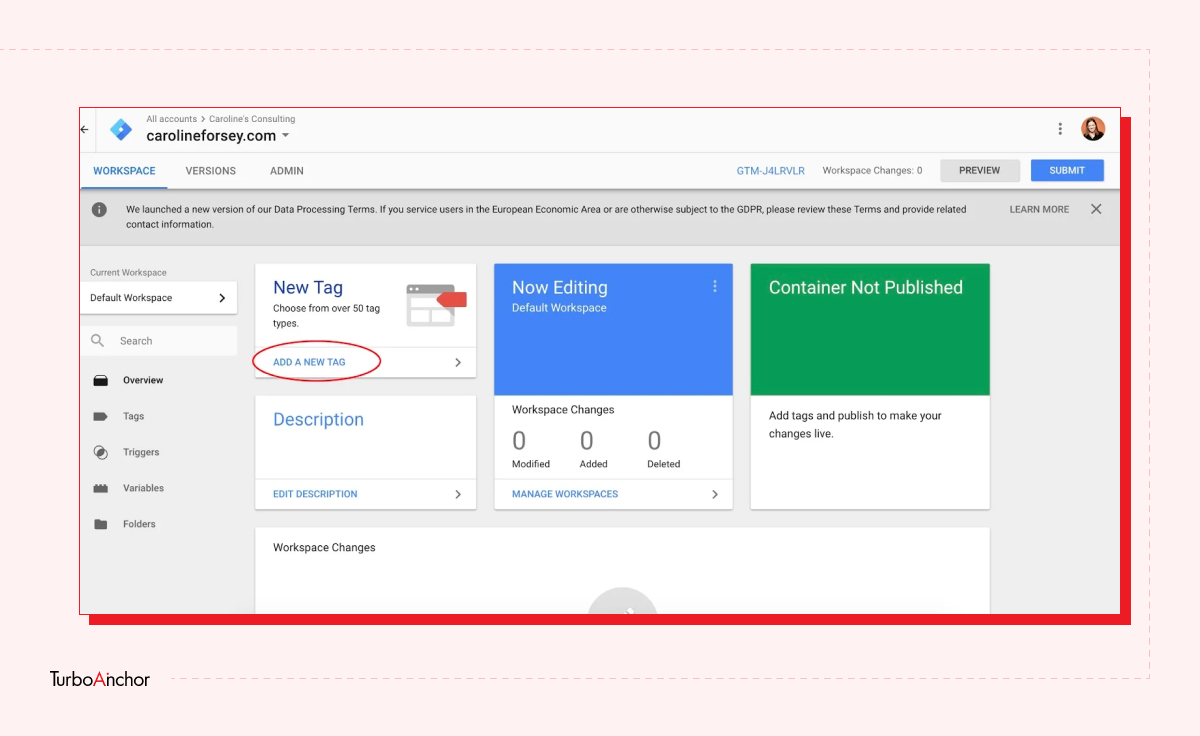
Here is what you need to know to set up a free GTM account. Follow the steps below.
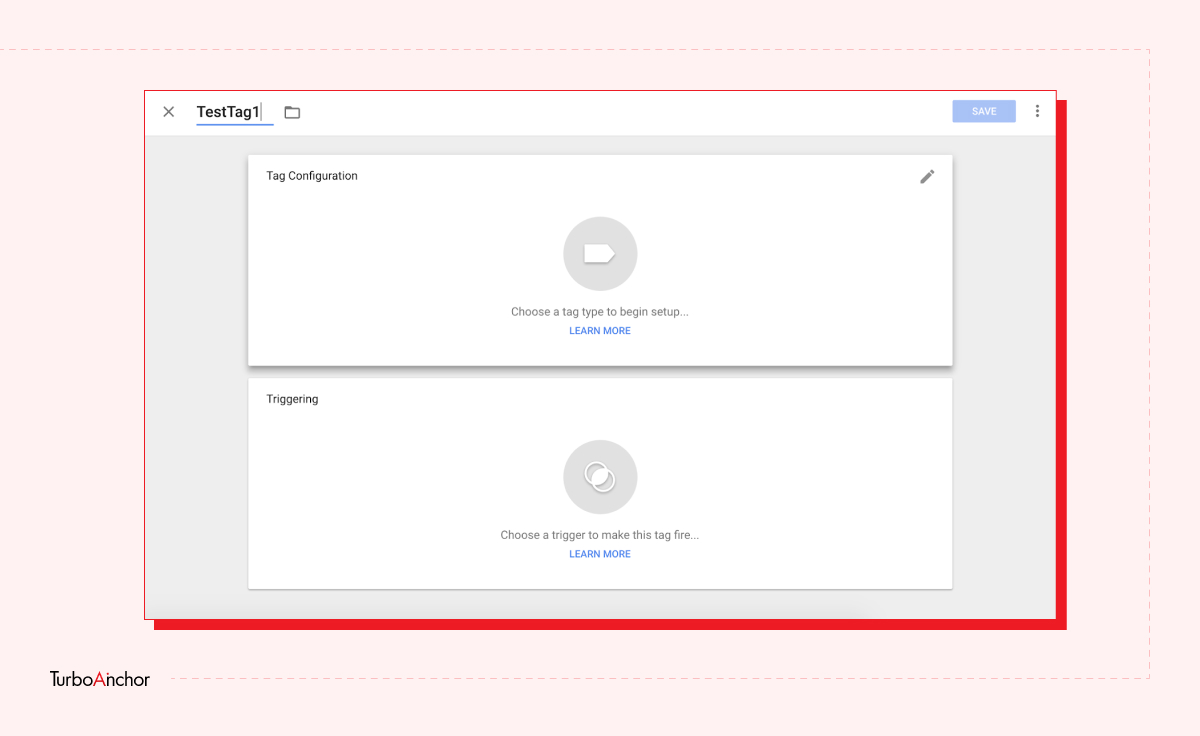
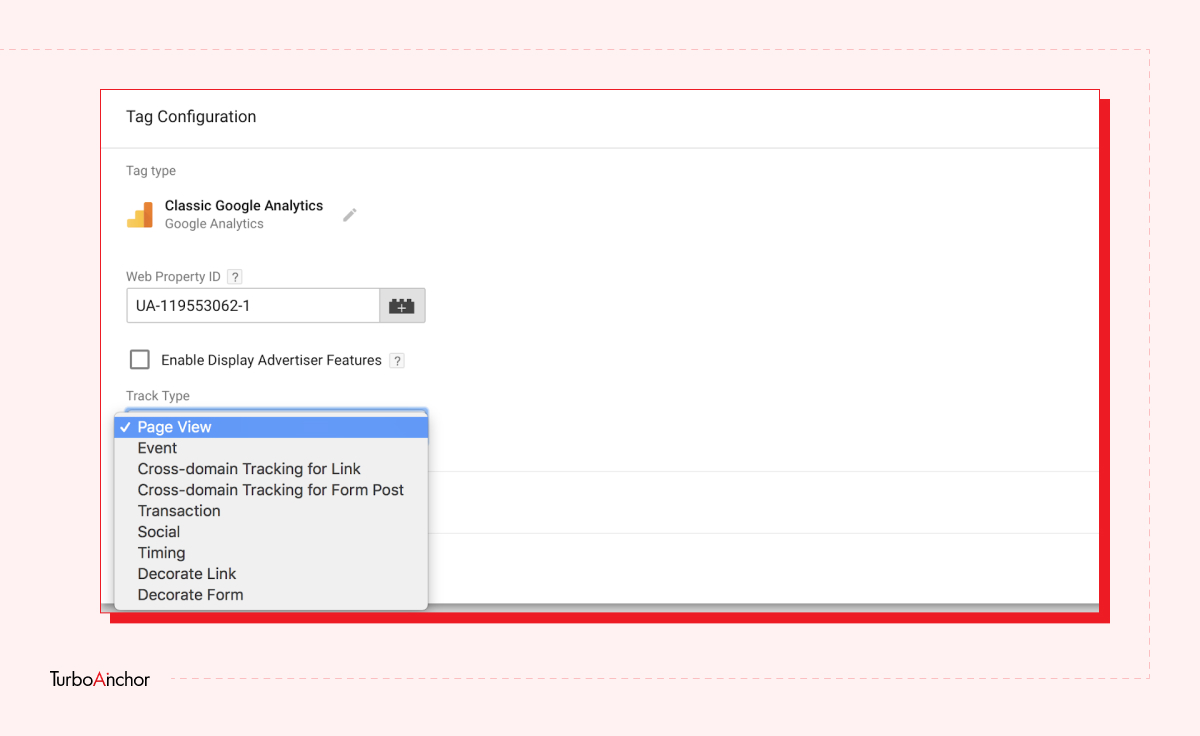
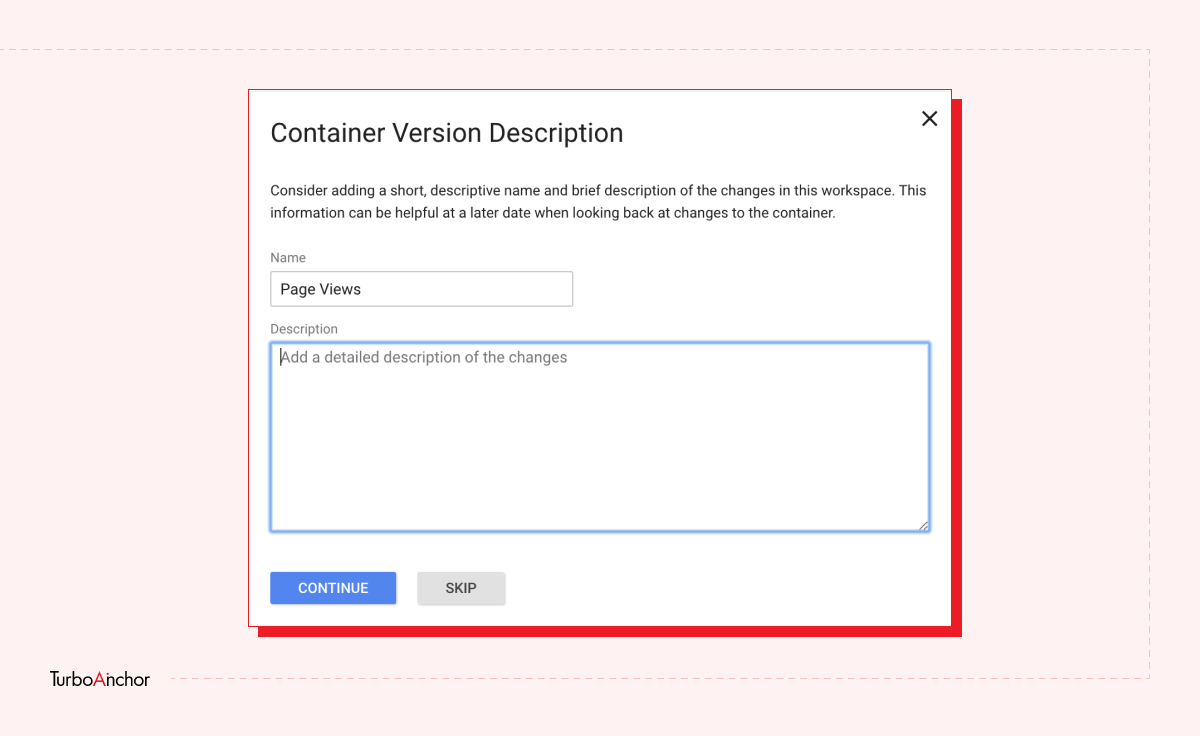
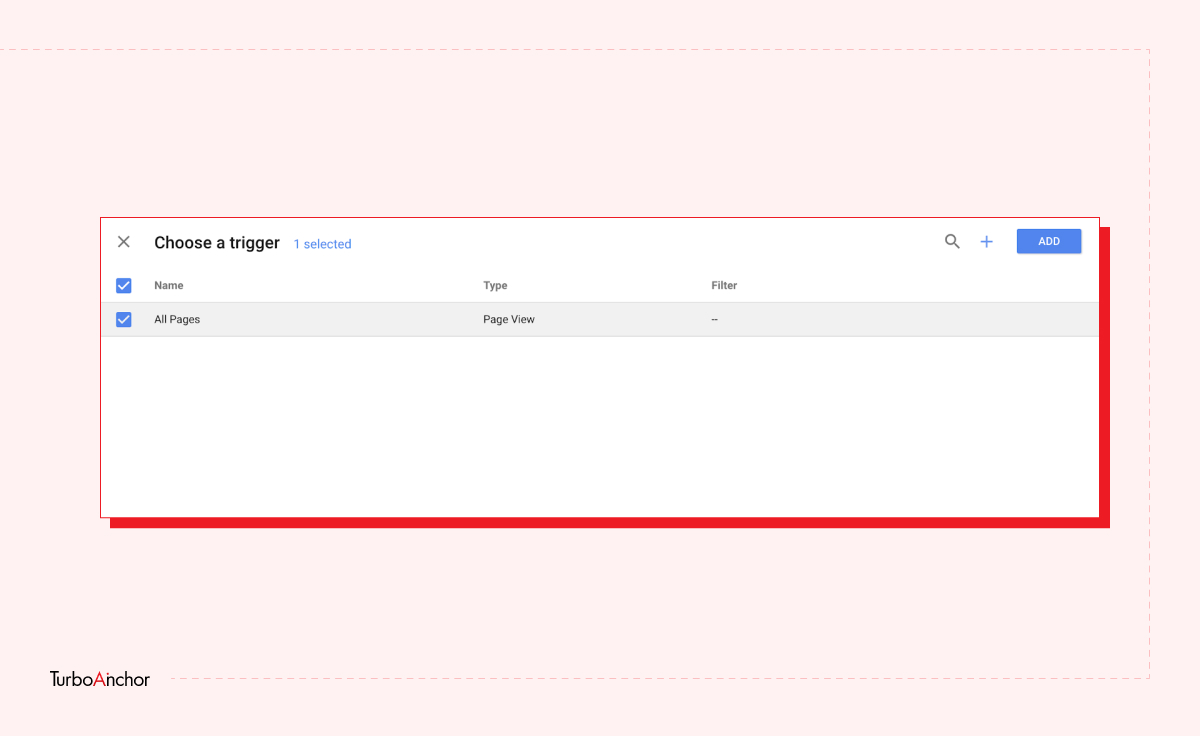
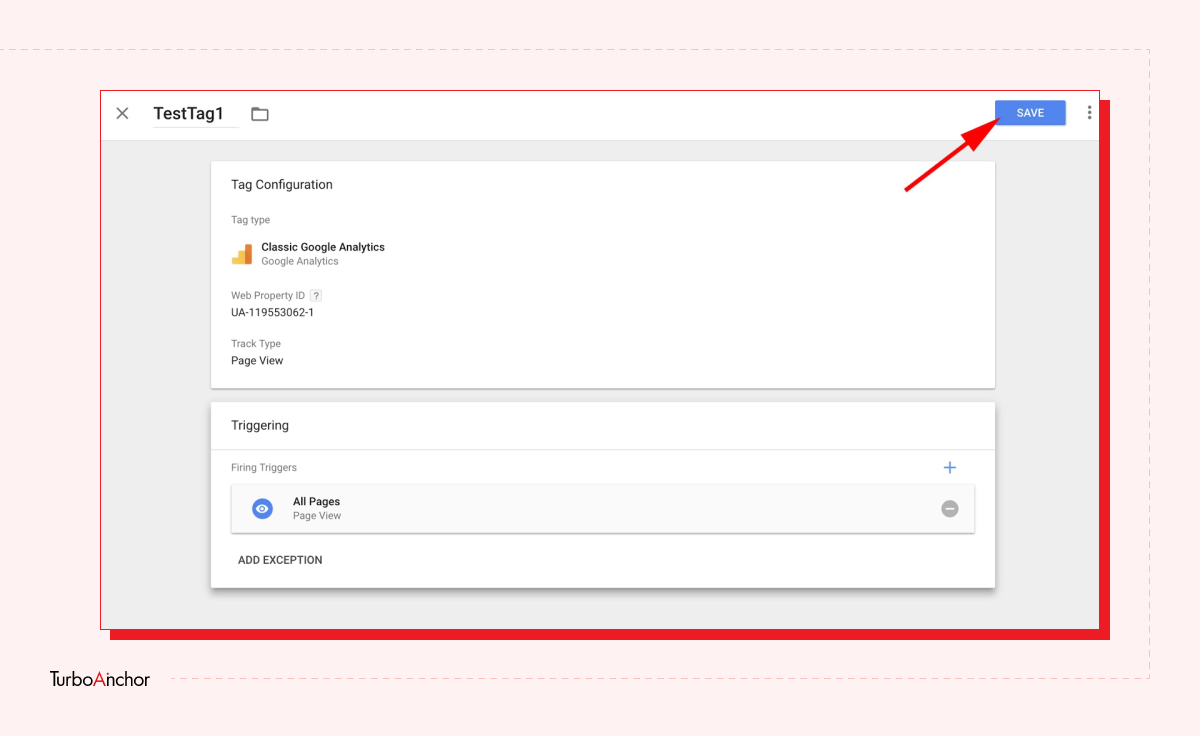
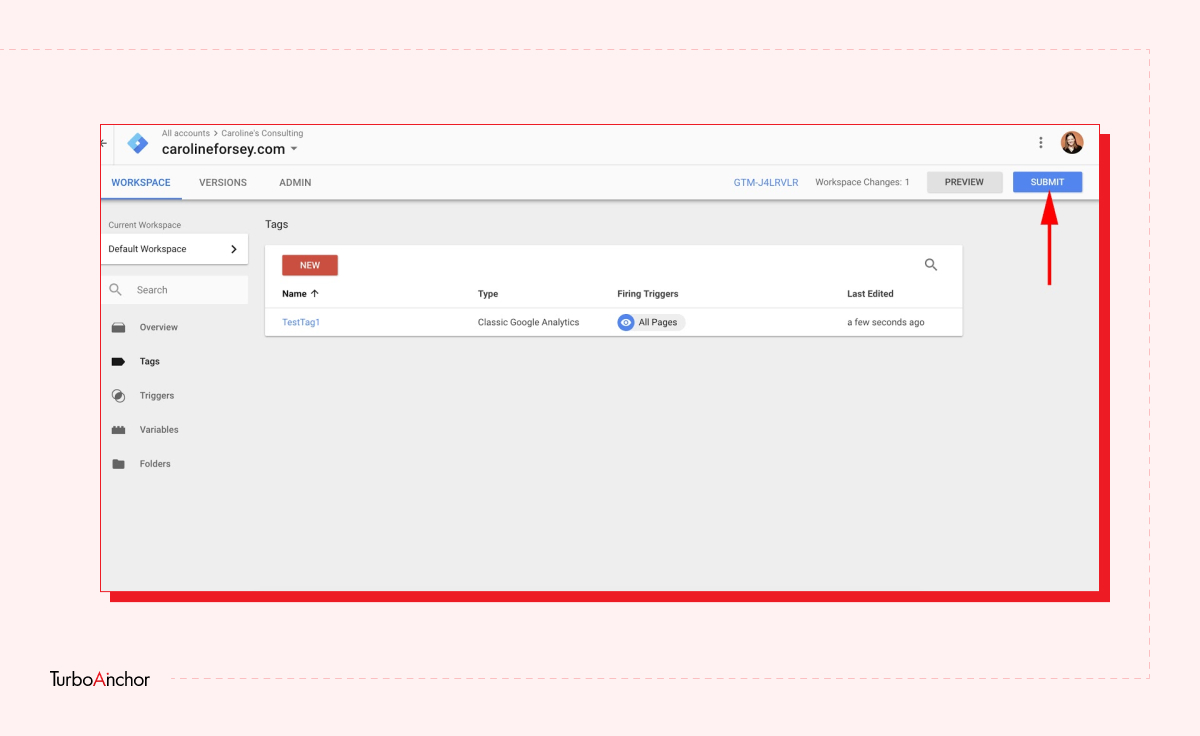
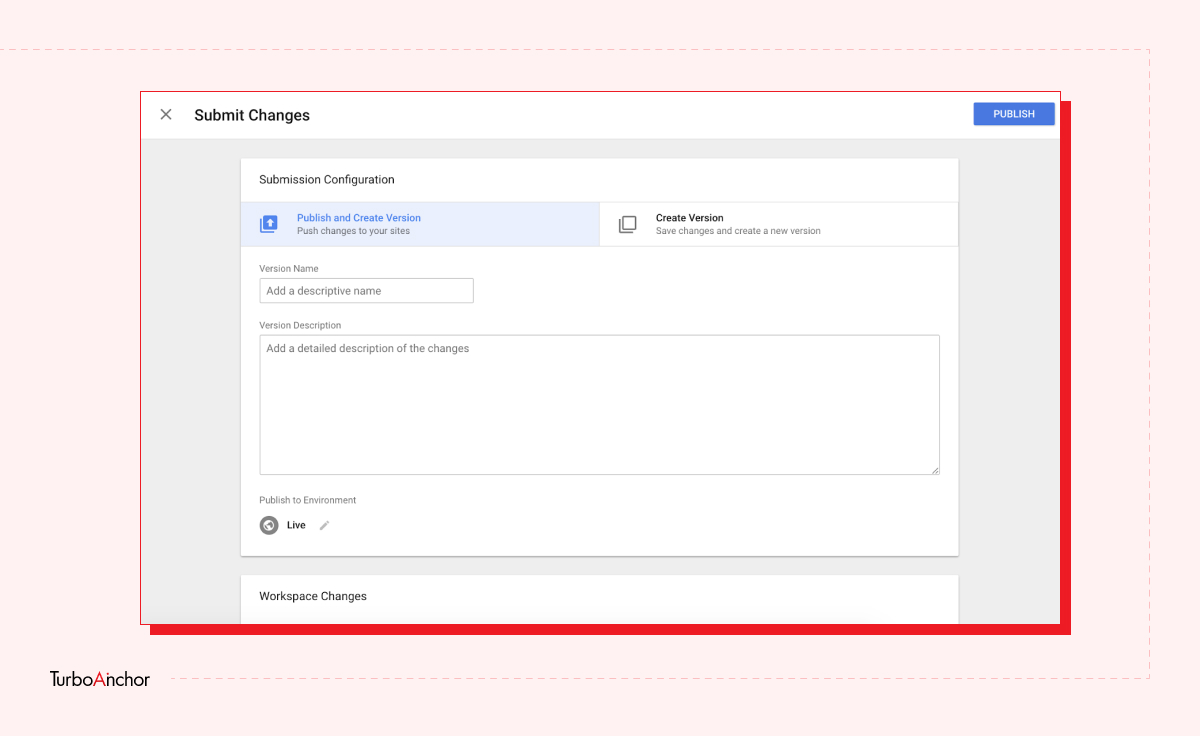

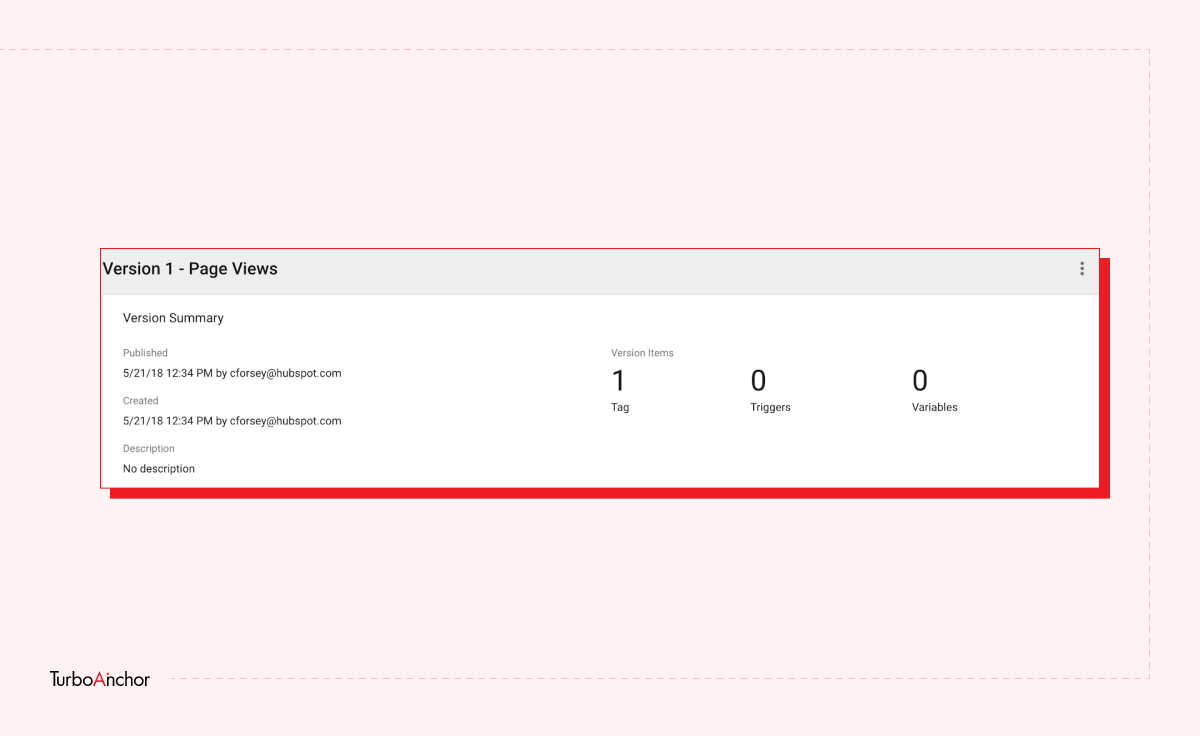
GTM is easy-to-use tag management and analytic tool, and it has a variety of benefits. A few of which are mentioned below:
If you are a marketer or an entrepreneur with no previous knowledge of coding, GTM is just the tool you need. It does not require any technical or professional coding knowledge. The GTM interface is user-friendly and easy to understand that allows the users to edit, remove, or add GTM tracking code without developers or coders.
GTM saves a lot of time, effort, and money. You no longer have to send emails back and forth to the developer, when you have to track additional events. You can simply track the codes i.e. the tags via the GTM platform.
GTM gives you complete control of who can make edits or changes. It can be read-only, editing to publishing rights, or give no access at all.
All the tracking code is controlled and managed in one place. It simplifies and improves the entire process of using tags.
GTM’s Preview Mode automatically shows you which tags are working and which one’s are not. As all the information is in one place it makes it easier to troubleshoot and correct the tag errors.
GTM might help your website load faster depending on how many tags you are using.
GTM is free and perfect for small and medium-sized businesses.
Some of the limitations of Google tag Managers are discussed below.
Often people tend to confuse Google Tag Manager and Google Analytics but here we have identified the key differences.
Google Analytics summarizes the website traffic data whereas GTM can not report on website traffic data. GA determines things like: “How many people visited the website at a specific time?”, ”How many leads has your website generated from Facebook?” and “Your Top-selling product”. GTM can not provide such information or insights because it is a tag management tool.
Google Analytics is a data source and GTM is not. Google Tag Manager is designed to send data from one data source to another, but GTM itself is not a data source.
GA collects various information related to the website, users, and devices via dimensions and metrics.
Google Tag Manager is a container log and GA is not. A container tag contains marketing and analytic tags and their relevant triggers and variables. A container log provides all the functionality of GTM to run and deploy the tags on the website.
You can use GTM without GA and vice versa. They are not dependent on each other.
GTM is used to add, edit, enable or disable tags from the website or a mobile app. It gives control over “when and where the tag should fire?”, “ what the tag should do when executed?”. Whereas, GA does not offer such functionality.
GTM is a management tool that is used to manage tags and GA is used to store, process, and report on website traffic data. These two can be replaced by each other.
Google Tag Manager is a powerful, useful, and easy-to-use tag management tool. It is a centralized platform that provides you with opportunities for improving your website and keeping up with digital marketing trends.
Google Tag Manager can track the following:
You can use Google Analytics without Google Tag Manager and vice versa. If you want to use the two together you will have to set up each account separately. GTM and GA are similarly implemented on the website using JavaScript code snippets.
Although Google Tag Manager is an easy-to-use tool, you still need to have basic technical knowledge about tags, and how to set up the tags, triggers, and variables. To set up event tracking you need some knowledge about what events are, and what data you can track with events.
References:
[1] Usage statistics of tag managers for websites – W3Techs