Design Thinking has gained popularity and attention over the past decades. It is now viewed as an exciting new model for dealing with problems in almost every field be it medicine, education, business, or IT. Design Thinking enables the designers to understand the needs, wants, and preferences of the customers in a better way. It helps us by building customer empathy, challenging assumptions, and using the solution-based approach to solving problems.
In this blog post, you will learn about design thinking, its importance, and its relevance to UX design.
Table of Contents
ToggleThe Origin of Design Thinking
IDEO (Innovation Design Engineering Organization) is often credited with inventing the term design thinking and its practice. However, design thinking has been evolving since the 1960s. IDEO has been practicing human-centered designs since 1973.
Leading up to the advent of design thinking there were many approaches. Richard Buchanan in 1992, framed the concept of moving from simple problems to wicked problems. Wicked problems are complex, open-ended, and vague [1].
What is Design Thinking?
Design thinking is a mindset and it can not be summarised in a one-line definition. It is a method, a strategy, and a way of seeing the problem. According to IDEO, Design Thinking is the intersecting point of human desirability, technological feasibility, and economic viability. The academic director of Hasso Plattner Institute of Design at Stanford (d.school), says that “Doing is everything”. This mantra is rooted in design thinking, and he describes:
“Design Thinking is to not have a failure of fear, to have a bias towards action and empathy toward whom you are designing for”
Also Read: What is UI UX Design? Difference Between UI & UX
Principles of Design Thinker: Designer’s Mindset
Some of the essential principles of the design thinking method include:-
Humans do inventions and innovations for humans:
Design Thinking is a human-centered method and the core purpose of every invention is to solve human problems. However, invention alone is not sufficient. It should be accompanied by innovation. For instance, Thomas Edison is famous for his invention of the light bulb and R&D lab. However, this alone did not lead to his success. Edison worked on the electricity generation, design of the lampstand, wiring, and switches to support his invention of the light bulb and bring it to practical use. This example is consistent with the definition of Innovation “long process of bringing a good idea to widespread and effective use”.
Combining divergent and convergent thinking:
Thinking divergently means breaking away from the conventional pathways and thinking of all possible choices. Contrarily, convergent thinking means focusing on the few feasible choices.
Related Read: Understanding UI Branding Principles for Better Brand Recognition
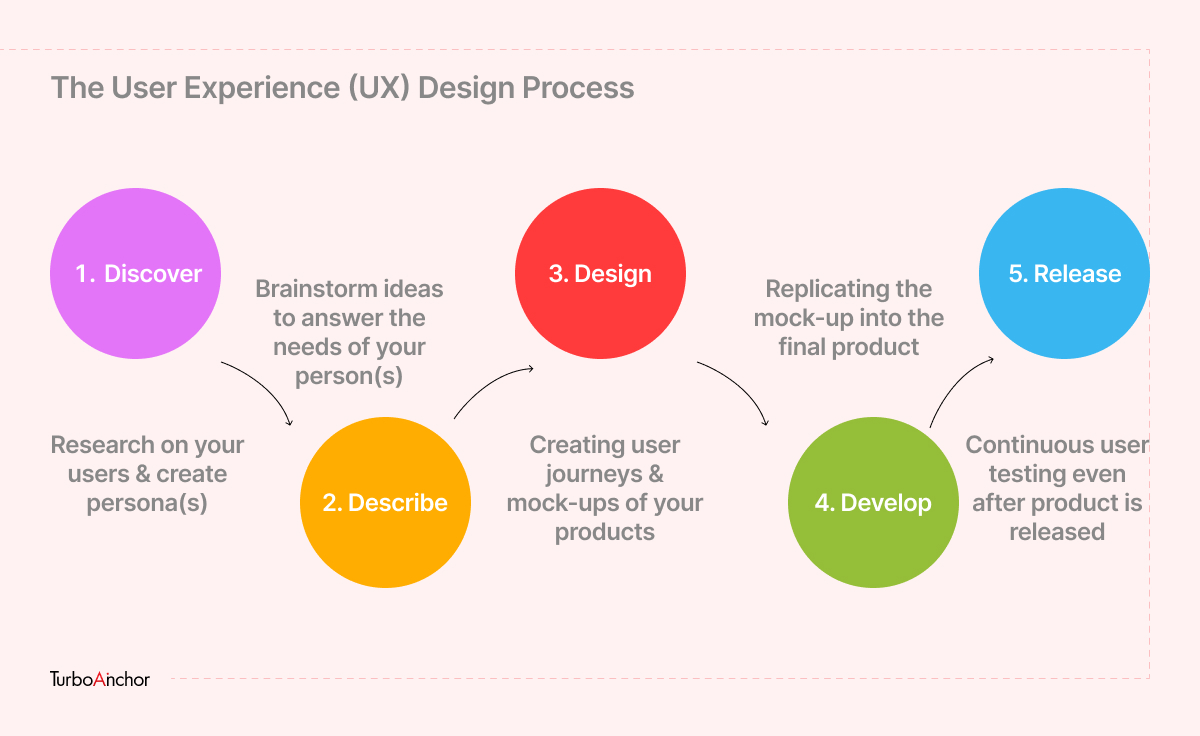
The Five Phases of Design Thinking
Design Thinking phases are not sequential. The five stages of design thinking as explained by the Hasso-Plattner Institute of Design are flexible and iterative. The five stages in the design thinking process are explained below:
Phase 1: Empathize
The first phase of the Design Thinking process is to empathize with the user’s needs. Walk in the shoes of your customers to understand their needs and preferences. The first stage of designers converting into detectives is gathering information about the users’ lives, what they do, their likes and dislikes, and how you can add value via your product or service to their life.
The ultimate goal of this stage is to understand their nature and not assume anything about your users. Undoubtedly, empathy is a critical starting point. However, it is of utmost importance to deeply understand the needs, barriers, attitudes, and aspirations of the consumers to uncover the existing problems and the solutions. And this can be achieved by observing and engaging with the users to internalize their experiences and emotions on a better psychological level.
Phase 2: Define
It is the responsibility of a designer to define the problem and design your product/ service around the customer and you should not try to wrap the user’s mind around your solution. When the problem is discovered the Design Thinking practitioners must answer these questions to develop a user-centric problem statement.
- Which problem/issue matters the most?
- Which problem requires immediate attention?
- What is the feasible strategy/plan?
Phase 3: Ideate
The third phase of Design Thinking is ideation, it is the process of generating, developing, and testing ideas. That can be done by tools such as:
- Brainstorming
- Word banking
- Mind mapping and landscape mapping
- Post-it Notes
The rote to distinct ideas is Divergent Thinking as it finally leads to innovation. To achieve Divergent Thinking, it is important to have a diverse group of people in the designing team. Interdisciplinary teams move into a structured brainstorming process. Answering one challenging question at a time can generate hundreds of new ideas.
Phase 4: Prototype
The results of the ideation process are prototypes. It means transforming ideas and thoughts into tangible artifacts. The prototypes do not have to be perfect and cent percent accurate. The whole concept of prototypes is to view the ideas in a tangible form to build the next ideas on them. Low-fidelity Prototypes consist of sketches, paper models, or storyboards. High-fidelity prototypes introduce UI elements and how the users might interact with the design. By the end of the fourth stage, the design team has a better idea of the further direction of the product/service. It understands the existing issues and problems with the prototype, and a clearer view of how real users would react to it.
Phase 5: Test
The final stage of the UX Design Thinking Process is Testing out the solutions. Although it is the final phase it is not the end of the Design Thinking process. The results of the tests are either confirmed or come up with some challenges yet to be solved. And the loop starts once again. As mentioned before, Design thinking is not sequential, rather it is a non-linear, and iterative process, that helps the designers to examine the results and return to the previous steps to make the necessary changes and improvements.
Suggested Read: What Is UX Research & How Is It Done?
UX Design and Design Thinking
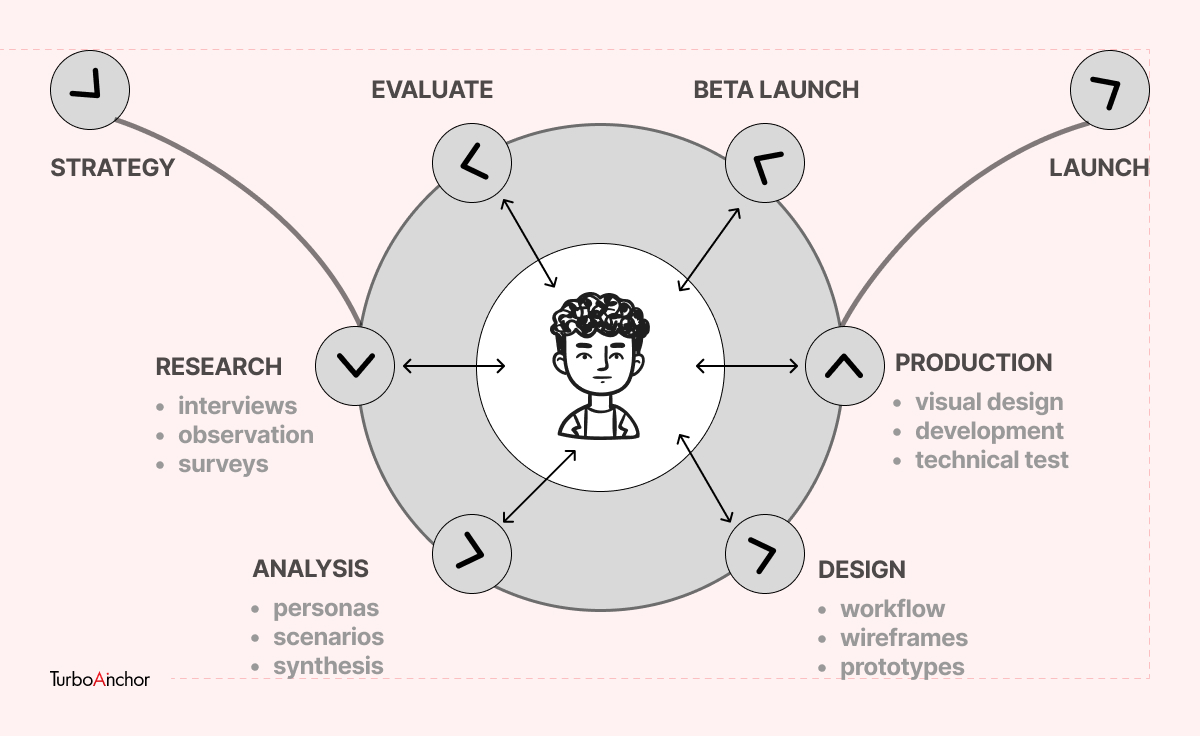
Design Thinking is often seen from a management perspective to create a better solution to the user’s problems and UX design focuses on creating better products and services. Nevertheless, UX design and Design Thinking on the core share the same idea to create a better user experience by focusing on deeply understanding the consumer’s preferences and what they value.
Develop a clear and accurate problem statement to kick start the ideation process and build on those ideas to create tangible prototypes. All of this is done to create a satisfying and personalized experience for the consumers that meet their expectations.
Conclusion
UX Design Thinking Process is well known and extensively used. Design Thinking is an outstanding way to solve the problems of consumers. It is an iterative process that instills a deeper collaboration among the designers and the other departments of the organization and creates a better, stronger, and diversified team.
It also begins the collaboration process between the users and the designers, no other method can uncover the true needs of the users. UX design and Design Thinking are the two sides of the same coin because of the user-centric approach that is the basis of both.
UX Design Thinking Process – Frequently Asked Questions
What is Stanford 5 step design thinking process?
The stages of Design Thinking by Stanford d.school are:
- Empathize – Understand your users’ preferences
- Define – Develop an accurate problem statement
- Ideate – Innovative and Unique ideas
- Prototype – Create a tangible product
- Test – Testing the solutions created
What are the key concepts of user experience design?
The key concepts of User Experience design are mentioned below:
- Empathy – UX designers when practicing empathy can put themselves in the users’ shoes and learn more about their lives and the problems that need to be solved.
- Strategy – Designing effective solutions to difficult problems by crafting a UX strategy.
- Usability – UX designers should consider accessibility, psychological factors, and mental models when designing optimal usability.
- Inclusivity – Inclusive designs ensure a variety of voices and opinions from a diverse population.
- Validation – User feedback is the most crucial concept in UX design. Even after the product or service is launched getting user validation is important.
Also Read:
References:
[1] Wicked Problems in Design Thinking – Scaruffi