As IoT steps foot in the world of technology, we have observed that it is proving to be quite a revolutionary phase. Traditional telecommunication providers are also witnessing small startups skyrocketing to new heights because of adapting to these new technologies and driving automation and digitalization to unprecedented levels.
These monumental changes are being made to numerous industries by IoT, and established powerhouses are taking notice. Choosing the right technology for your needs remains critical as companies respond to this revolution with new and innovative IoT applications. According to reports, the number of cellular IoT connections will rapidly expand from 1 billion to 4.1 billion in 2024. [1]

Suggested Read: All You Need To Know About IoT Solutions
Let’s talk about NB- IoT vs LTE- M
To be specific, NB-IoT & LTE-M are the most common technologies used today. NB-IoT is deployed in both 2G & 3G networks & LTE-M can specifically for 4G. Both have proven valuable and reliable in real-world IoT situations, which has led many telecommunication companies worldwide to install at least one of these technologies or plan to shortly. Research shows that 47 LTE-M and 98 NB-IoT networks are active worldwide as of November 2020. [2]
For a more detailed understanding let’s dig deeper,
What is NB- IoT?

As the name suggests, Narrowband IoT uses a single narrowing of radio frequencies to help lower power consumption at the cost of available bandwidth. According to the LTE standard, it has a maximum bandwidth of 200kHz.
NB-IoT aims to extend coverage further than possible with existing cellular technologies. It can be accomplished by uplink repetitions and different bandwidth allocation configurations within NB-IoT. By reducing the power consumption of connected devices, NB-IoT increases system capacity and bandwidth efficiency, especially in remote locations not easily covered by traditional cellular technologies.
The NB-IoT has many benefits regarding indoor coverage, low cost, long battery life, and high connection density. In other words, it’s ideal for devices located in buildings, in remote locations, and even underground in some cases. For many use cases, devices connected via NB-IoT can have over ten years of battery life.
The following are some NB-IoT applications,
- Smart Cities
- Smart Buildings
- Smart Farming
- Waste management
- Manufacturing automation
What is LTE-M?
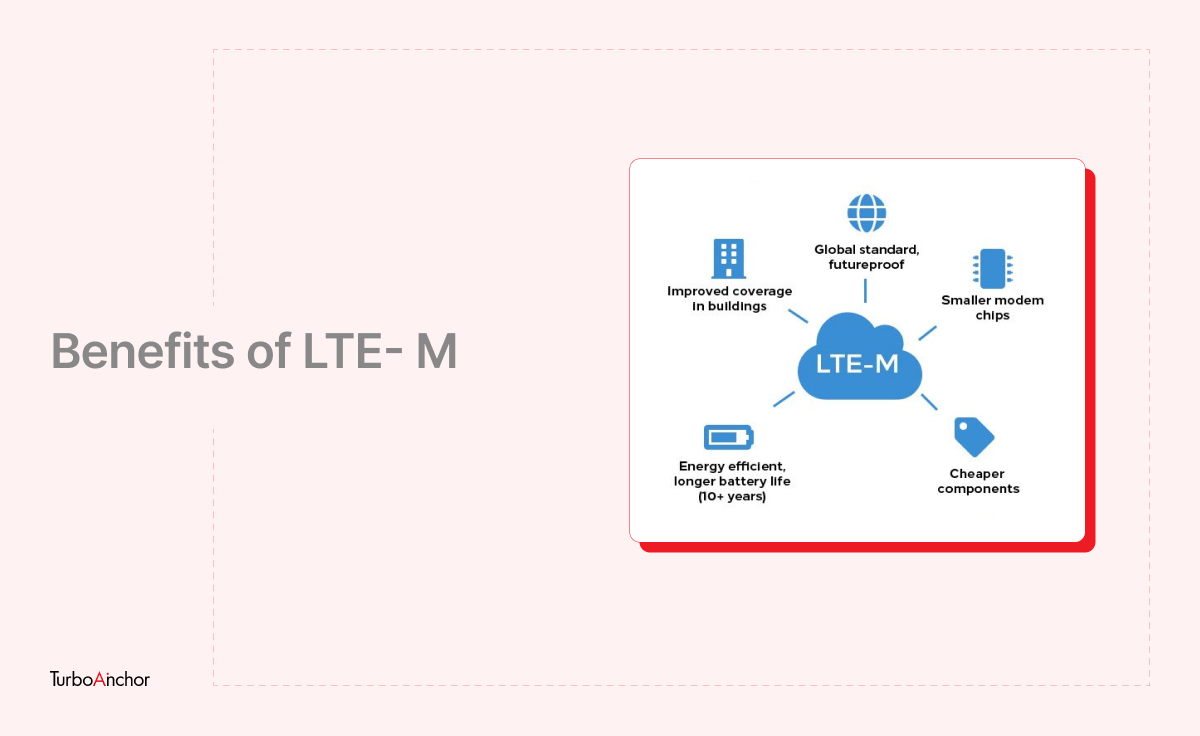
LTE-M specifically refers to LTE CAT-M1, suitable for the IoT. It’s a low-power wide-area technology that supports IoT through lower device complexity. The device connects directly to a 4G network without a gateway and uses only batteries. Note that the term LTE-M refers to only the addition of LTE to 4G technology, not that every 4G device supports LTE-M automatically.
There are some similarities between LTE-M and NB-IoT. For instance, LTE-M’s design supports a longer battery life of up to last 5 to 10 years. Also, LTE-M can perfectly coexist with other cellular offerings like 2G, 3G, and 4G. So that means devices get all of the benefits of a mobile network’s security and privacy features.
Suggested Read: A Quick Guide On What Is IoT Security?
LTE-M has another advantage over standard GSM technology in that its penetration of radio frequencies is better, resulting in better indoor coverage. It offers better coverage in tight places where there are poor connections using 2G/3G/4G networks, which means that objects in these places can still upload data in real-time.
The following are some LTE-M applications,
- Asset Tracking
- Wearables
- E-health solution
- Low-density sensors
Comparison Between Both Technologies
FAQs
What is the difference between LTE-M and NB-IoT?
The key difference between LTE-M & NB-IoT is that LTE- M steps where NB-IoT lacks. Both play an essential role in connecting a range of IoT devices. LTE-M is better in average coverage conditions, and NB-IoT is better in poor coverage conditions. While speaking of mobility, LTE-M is suitable for static and mobile devices. At the same time, NB-IoT is only ideal for static.
What is the range of NB-IoT?
NB-IoT has the lowest range and coverage capabilities.
Like, 10 km. It focuses mainly on the type of devices installed at places far from the usual reach of cellular networks. For instance, underground or basements.
What is LTE-M coverage?
LTE-M allows IoT devices to connect directly to a 4G network without a gateway and while running on batteries. While speaking of range in terms of maximum distance between the tower and the IoT device is around 1 km in urban areas and about 10 km in rural areas.
Is LTE the same as LTE-M?
Well, similar to LTE, LTE-M allows your network & data transmission. Still, the difference between them is the simplicity of LTE-M as it exchanges data transmission rate for better power efficiency and signal range.
Is NB-IoT 4G or 5G?
NB-IoT is currently being classified as 5G technology. The International telecommunication Union recognized 3GPP NB-IoT as an officially supported standard. That means NB-IoT networks should increase bandwidth performance, higher connected device densities, and lower latency numbers compared to older cellular technologies.
Is WiFi an LPWAN technology?
LPWAN, also known as a Low-power wide-area network, enables multiple wireless connections covering long distances with minimum power consumption and maintenance. Compared to Wifi or ZigBee.
The following are representative technologies of LPWAN,
- NB-IoT
- Long Range (LoRa)
Conclusion
IoT offers you a variety of possibilities, technologies, and solutions, so if you’re still unsure which option best suits your application. Whether you go with an LTE-M or NB-IoT solution doesn’t matter until it’s up to your IoT needs. There might be situations where you might end up needing both technologies.
For example, smart city applications, and waste management, where sensors report how full a city dumpster is. No one’s some wizard, so it’s impossible to predict which LPWAN technology will work out the best. But looking at current statistics, both LTE-M and NB-IoT can have clear uses in certain situations.
Also Read:
- Best IoT Solutions For Enterprises
- 6 Prominent Benefits of IoT For Consumers
- How IoT in the supply chain can help manufacturers?
References:
[1] Ericsson Mobility Report – ericsson.com
[2] LTE-M and NB-IoT networks active worldwide – GSMA
